Myofascial Pain Syndrome (MPS) is a chronic muscle disorder that results in local pain, stiffness, and tender points. It normally affects the neck, shoulders, back, and hips and disrupts daily living and general quality of life. MPS may develop as a chronic and intractable illness, and, therefore, early diagnosis and specialized treatment of Myofascial pain are essential.
Understanding Myofascial Pain Syndrome
MPS is a condition in which the muscle fibers become tight and irritable in the form of tight bands known as myofascial trigger points. These points block the flow of blood, interfere with the work of muscles, and lead to pain in the local and remote locations. In contrast to the common muscle soreness, MPS is associated with specific pain generators that require a close clinical assessment and a systematic treatment for myofascial pain to be able to attain permanent relief.
Causes of Myofascial Pain Syndrome
Muscles can be kept in a tense state and develop myofascial trigger points because of a number of mechanical, physical, and psychological factors. To effectively treat and prevent the recurrence of these underlying causes, it is necessary to identify them.
Muscle Overuse and Repetitive Strain
Frequent movements, prolonged immobility, or excessive physical activity strain muscle fibers. This causes micro-injuries, a lack of oxygen, and myofascial trigger points in the long run. The occupations associated with repetitive movements and athletes who use repetitive movements are particularly vulnerable to chronic muscle strain.
Poor Posture and Ergonomic Issues
Spending considerable time in an awkward position causes disbalanced tension in muscles, particularly the neck, shoulders, and lower back. Poor workstation arrangement or excessive use of the devices may lead to long-term muscle imbalance, which predisposes the likelihood of experiencing MPS symptoms and restriction of functionality.
Muscle Injury and Trauma
Localized muscle problems may begin directly through such injuries as muscle tears, falls, or whiplash. Incomplete healing can lead to the persistence of the trigger points to continue their pain generation even after the original injury has disappeared.
Emotional Stress and Muscle Tension
Psychological stress maintains the muscles in a contracted state by raising the activity of the nervous system. Stress that is chronic may keep muscles tight, decrease relaxation, and increase pain responsiveness, which aggravates MPS with time.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Movement patterns may be altered and specific muscles overloaded by spinal disorders, joint issues, or inflammatory disorders of the system. These compensatory mechanisms predispose nearby groups of muscles to MPS.
Symptoms of Myofascial Pain Syndrome
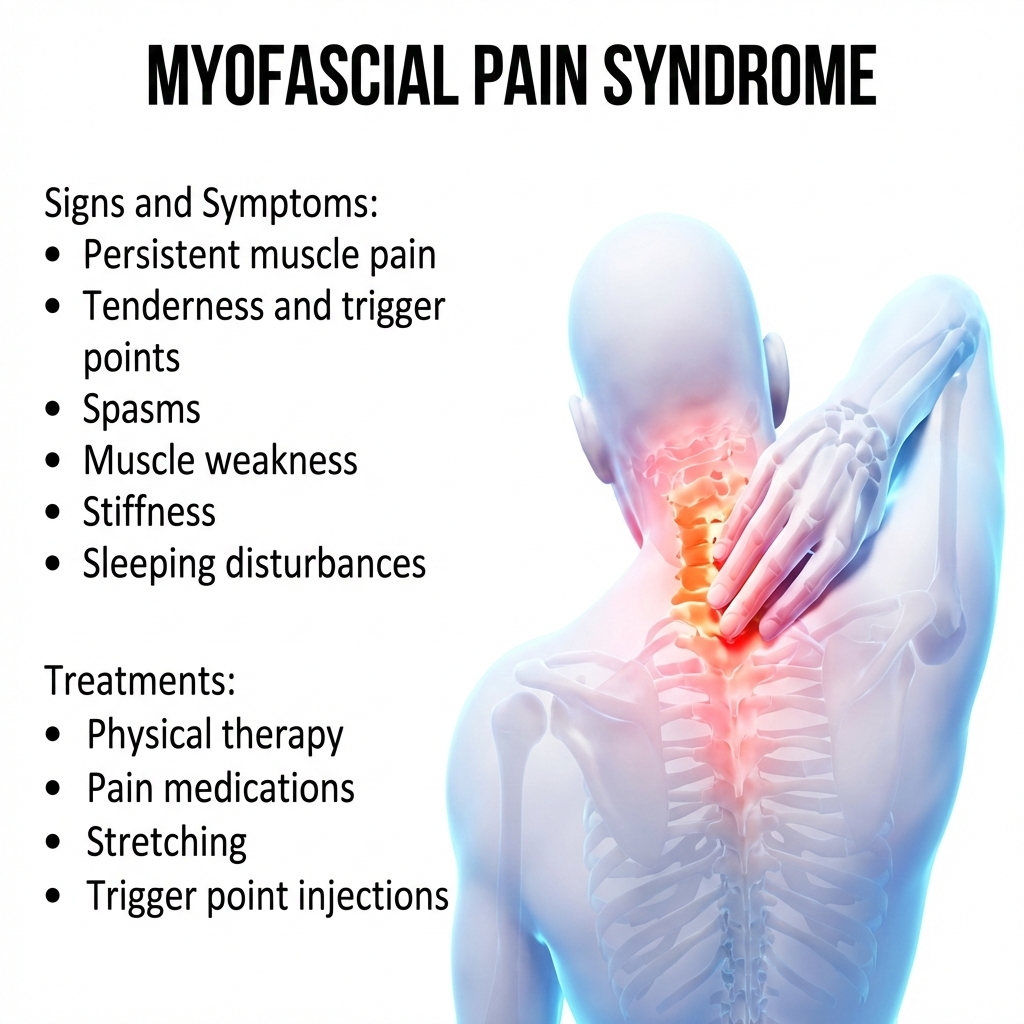
The MPS symptoms are variable in intensity and normally localized, enduring, and activity-related. The identification of common patterns allows for a proper diagnosis and timely Myofascial pain treatment.
Deep, Aching Muscle Pain
Patients usually complain of a persistent, severe ache within affected muscles. The pain can become use or position-dependent, or stress-dependent, and in most cases cannot be relieved by mere rest.
Trigger Points and Muscle Knots
Characteristic features are tender nodules in tight bands of muscles. When pressed, these myofascia trigger points cause pain and may elicit sensations elsewhere.
Referred Pain Patterns
The pain is often perceived at a distance from the trigger point. As an example, the presence of shoulder trigger points can produce the sensation of pain in the head or arm and mislead the diagnosis and imitate nerve or joint disorders.
Muscle Stiffness and Reduced Mobility
Continued muscle tightness limits the range of motion and flexibility. This rigidity distorts the pattern of movement and makes the daily chores more exhausting.
Pain Aggravated by Activity or Stress
MPS symptoms are usually aggravated by physical activity, long periods of inactivity, or emotional trauma. Pain may also exacerbate and disrupt sleep and functioning capacity without treatment.
How Myofascial Pain Syndrome Is Diagnosed
A detailed clinical examination is used to diagnose it, and not through imaging. It is necessary to identify trigger points and to eliminate other causes.
Clinical Evaluation and Trigger Point Examination
Detailed physical examination reveals tight bands, tender nodules, and pain designation. Recreation of an already known pain on palpation is a strong supportive feature of an MPS diagnosis.
Differentiating Myofascial Pain Syndrome From Other Conditions
MPS should be differentiated from fibromyalgia, radiculopathy, and joint disorders. In contrast to fibromyalgia, MPS is confined and associated with trigger points as opposed to widespread pain.
Role of Imaging and Diagnostic Tests
The imaging studies are typically normal but may exclude structural issues. These are tests that uphold clinical findings but do not directly confirm MPS.
Treatment Options for Myofascial Pain Syndrome
The multimodal approach, which addresses muscle dysfunction, pain modulation, and lifestyle factors are essential in effective management.
Physiotherapy and Stretching Techniques
Specialized physiotherapy enhances posture, movement patterns, and flexibility. Stretching exercises alleviate tension, enhance circulation, and inhibit reactivation of trigger points.
Trigger Point Therapy and Dry Needling
Manual trigger point release and dry needling make painful nodules inactive and restore muscle functioning. These methods directly enhance the circulation of blood and minimize neuromuscular irritation.
Medications for Myofascial Pain Relief
The useanti-inflammatoriestory or muscle relaxants can be used in the short term to alleviate flare-ups. When physical therapy and trigger point interventions are used along with medications, the latter are more effective.
Advanced Interventional Pain Treatments
Persistent cases may be regarded in terms of image-guided injections or regenerative therapies. The Myofascial pain treatment targets chronic inflammation in the muscles and assists in maintaining long-term symptom control.
Lifestyle Modifications and Ergonomic Correction
The key to a permanent recovery is postural training, ergonomic changes, stress control, and exercise. It is possible to handle bad habits and reduce the risk of re-emergence.
Preventing Myofascial Pain Syndrome
Prevention is based on the balanced use of muscles, good posture, daily stretching, and stress management. Muscle discomfort can be treated at the early stage to prevent the development of chronic pain.
When to See a Doctor for Myofascial Pain Syndrome
Ask a doctor to examine her in case the muscle pain continues longer than several weeks, becomes more severe with rest, or disrupts daily functions. Early detection enhances the recovery and decreases the chronicity.
Why Choose Alleviate Pain Clinic for Myofascial Pain Syndrome
Alleviate Pain Clinic is a non-surgical center providing evidence-based treatment of MPS. Individual treatment, sophisticated interventions, and skilled physiotherapy contribute to permanent alleviation of pain and functional recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
It can become chronic if untreated, but early and appropriate management often leads to significant improvement and long-term symptom control.
Myofascial pain involves localized trigger points, while fibromyalgia causes widespread pain and tenderness without discrete nodules.
Yes. Stress increases muscle tension and nervous system activity, which can aggravate myofascial trigger points and intensify pain.
Trigger point therapy combined with stretching and posture correction often provides rapid symptom relief.
While not always completely curable, consistent treatment and lifestyle modifications can achieve long-term symptom remission.




