
A sudden, sharp pain in the Pain in the Lower Back when bending over is an alarming experience that can leave you feeling concerned and immobilized. This type of pain often signals an underlying issue that requires attention. In this guide, we’ll delve into potential causes, common symptoms, immediate steps you should take, and effective treatment options to help alleviate lower back pain and prevent future occurrences.
Why Do I Feel Sudden Sharp Pain in My Lower Back When Bending?
A sudden pain in the lower back while bending is often linked to muscle strain, ligament sprain, or spinal disc stress. When the lumbar spine is forced into awkward positions, small tears can develop in muscles or connective tissues. Herniated discs, facet joint irritation, or sacroiliac joint dysfunction may also contribute. Patients frequently ask, “Why does my lower back hurt when I bend over?” – and the answer usually lies in a combination of poor posture, overuse, weak core muscles, and age-related degeneration.
Common Causes of Sudden Pain in Lower Back While Bending
Muscle Strain or Sprain
Sudden lower back pain while bending often results from muscle strain, disc issues, or nerve compression, requiring timely medical attention.
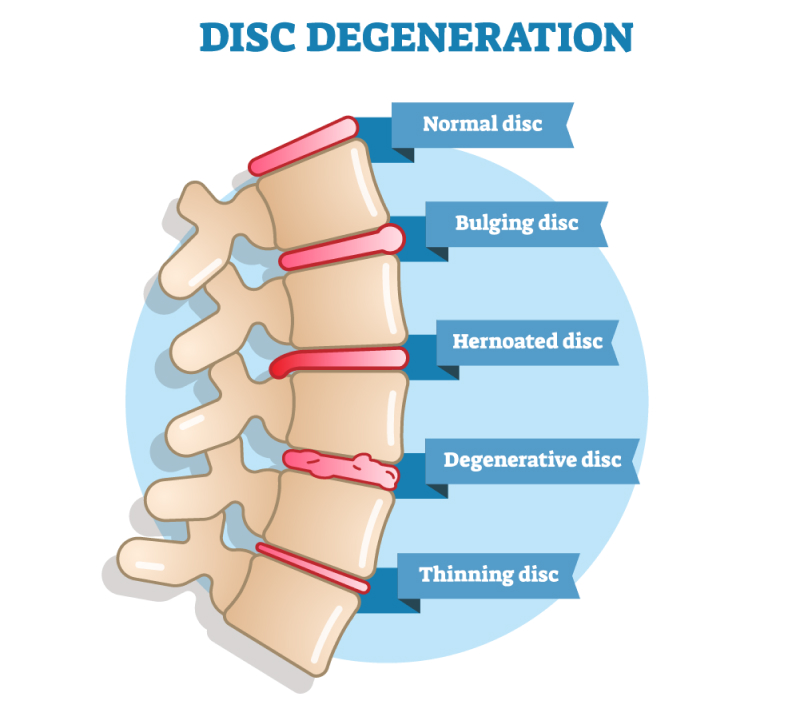
Herniated or Bulging Disc
- Description: A herniated (slipped) disc occurs when the inner core of a spinal disc pushes through its outer layer, potentially pressing on nearby nerves and causing lower back pain while bending forward.
- Triggers: Bending, twisting, or lifting improperly can cause a disc to herniate, often leading to sudden pain in the lower back while bending.
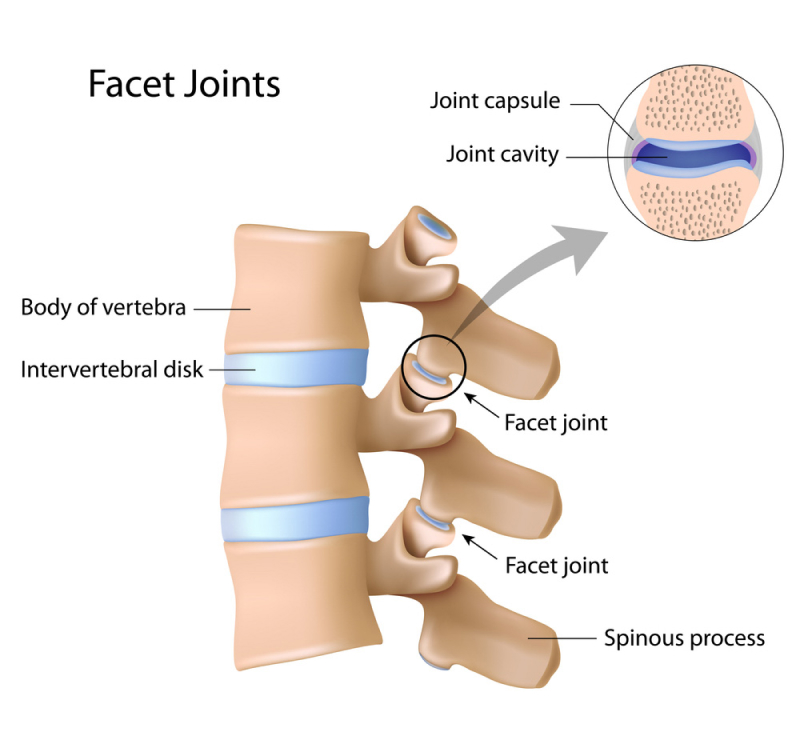
Facet Joint Dysfunction
- Description: The facet joints, which connect the vertebrae in the spine, can become irritated or misaligned, causing lower back pain.
- Triggers: Sudden movements or twisting and bending, especially when lifting heavy objects.
- Symptoms: Sharp pain when bending backward or sideways, localized pain near the spine.
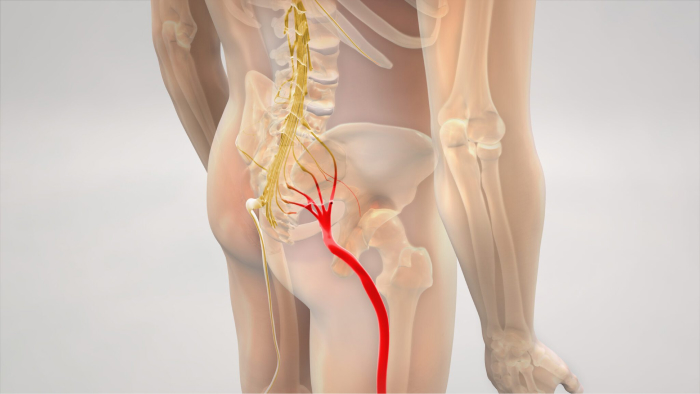
Sciatica and Nerve Compression
- Description: Compression of the sciatic nerve, often due to herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or muscle tension, can cause sudden, sharp pain in the lower back when bending over.
- Triggers: Bending, twisting, or prolonged sitting can aggravate sciatic nerve compression, leading to shooting pain in the back when bending over.
Symptoms: Sudden pain in the lower back while bending, radiating sharply from the lower back down the leg; tingling, numbness, or weakness in the affected leg.
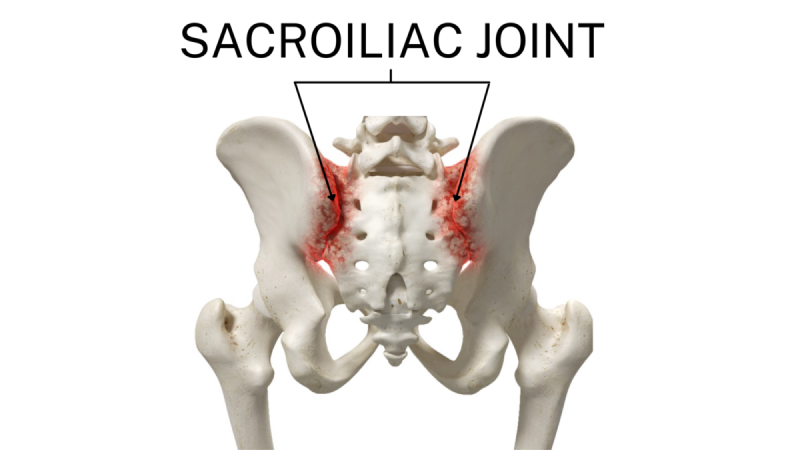
Sacroiliac (SI) Joint Dysfunction
- Description: The sacroiliac joints, located where the spine meets the pelvis, can become inflamed or misaligned.
- Triggers: Bending, lifting, or impact activities can exacerbate SI joint issues.
- Symptoms: Pain at the base of the spine, sharp discomfort when bending or twisting, and pain that may radiate to the buttocks or thighs.
Associated Symptoms
Knowing the symptoms associated with sudden lower back pain can help in pinpointing the cause and deciding on the appropriate action:
- Localized Sharp Pain: Often linked to muscle strain, facet joint issues, or SI joint dysfunction.
- Radiating Pain (Sciatica): Sharp, shooting pain down the leg is a hallmark of sciatic nerve involvement.
- Muscle Spasms: Common with muscle strains, which cause muscles to contract involuntarily, worsening pain.
- Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty bending, twisting, or standing upright could indicate joint or disc issues.
What Should You Do When You Experience Sudden Sharp Lower Back Pain?
When sudden lower back pain strikes, taking immediate steps can help reduce pain and prevent further injury:
- Stop the Activity: Avoid any movements that trigger or worsen the pain to prevent additional strain or injury.
- Apply Cold Therapy: Use an ice pack on the painful area for 15-20 minutes to reduce inflammation and numb sharp pain. Avoid applying ice directly to the skin; instead, wrap it in a cloth.
- Use Heat Therapy (After 48 Hours): Once the initial inflammation subsides, apply a warm compress to relax muscles and improve blood flow to the area.
- Gentle Stretching: Light stretches targeting the lower back, such as knee-to-chest and pelvic tilts, can relieve tension without exacerbating pain. Avoid intense stretching or any movement that increases pain.
- Practice Good Posture: Whether sitting, standing, or moving, maintain a neutral spine position to avoid further stress on the lower back.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relief: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can help reduce pain and inflammation in the short term.
Treatment Options for Sudden Sharp Lower Back Pain
If pain persists beyond a few days or worsens, it’s crucial to seek professional care to identify the root cause and receive targeted treatment. Here are some effective treatment options:
First Aid, Rest, and Gentle Stretches
When dealing with how to relieve sharp lower back pain, early intervention matters. The first step is rest, but complete bed rest is not advised. Apply cold packs within 24 hours to reduce inflammation, followed by heat therapy to ease muscle stiffness. Gentle stretches targeting the hamstrings and lower back muscles improve flexibility and circulation. Core-strengthening exercises help reduce the recurrence of sudden, sharp pain in the lower back when bending over. Avoid heavy lifting and maintain neutral spine alignment when sitting or standing. Practicing ergonomic posture during daily activities significantly prevents further strain.
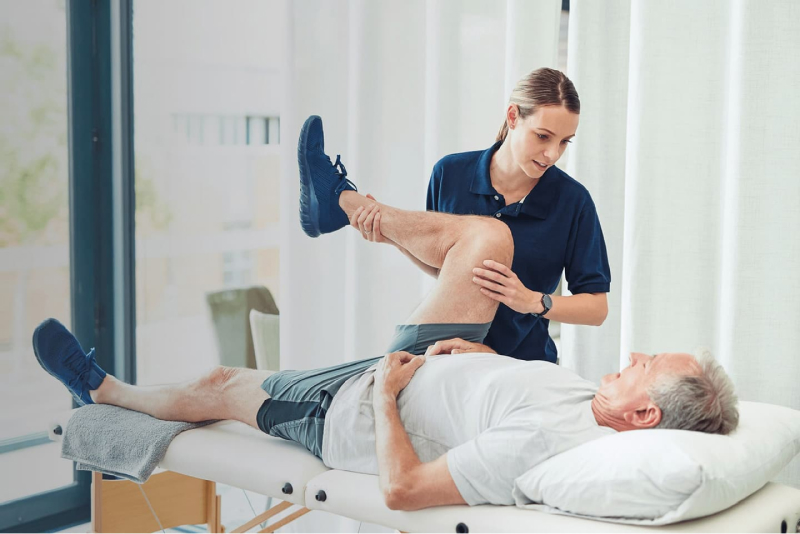
Physical Therapy
- Focus: Strengthening core muscles, improving flexibility, and correcting posture.
- Benefits: Physical therapy exercises build support for the spine and help relieve and prevent lower back pain.
- Techniques: Range-of-motion exercises, core strengthening, and functional training to reduce pain and restore mobility.
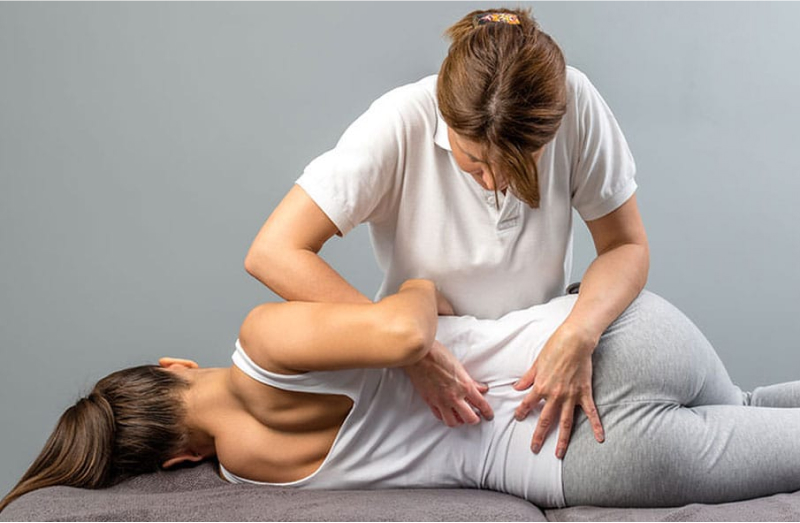
Chiropractic Care
- Focus: Realigning the spine and correcting misalignments in the lower back.
- Benefits: Alleviates joint-related lower back pain and improves range of motion.
- Methods: Manual adjustments and mobilization techniques, often combined with stretching and strengthening exercises.
Interventional Pain Management
Options
- Epidural Steroid Injections: Reduces inflammation and pain in cases of nerve root compression, such as sciatica or disc herniation.
- Facet Joint Injections: Provides targeted relief if facet joint dysfunction is diagnosed.
- SI Joint Injections: Treats sacroiliac joint pain and inflammation.
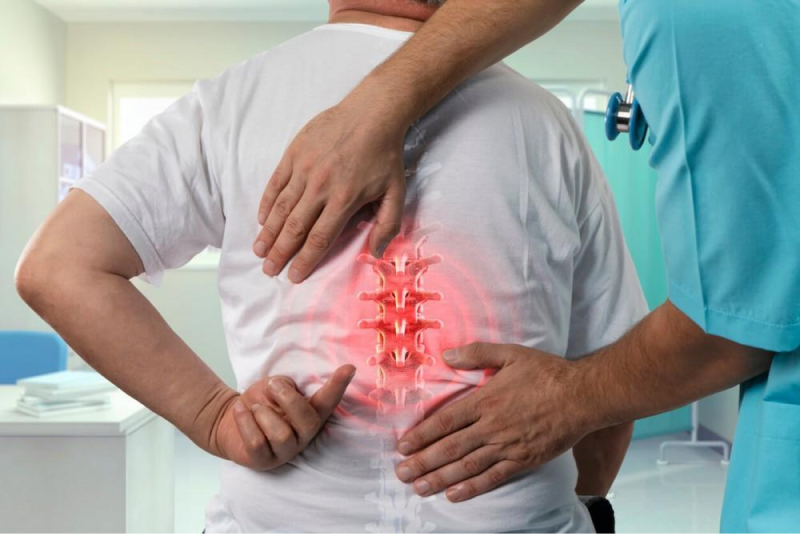
Benefits: Offers pain relief when conservative methods are insufficient, allowing for continued movement and physical therapy.
Medication Management
- Options: NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, and nerve pain medications may be prescribed depending on the pain cause and severity.
- Benefits: Provides temporary pain relief, especially during severe pain episodes.
- Precaution: Medications should be taken as prescribed to avoid dependence or side effects.

Lifestyle Adjustments and Ergonomics
- Focus: Modifying daily activities, adopting proper lifting techniques, and setting up ergonomic workspaces.
- Benefits: Reduces strain on the lower back, preventing future pain episodes.
- Recommendations: Regular stretching, maintaining a healthy weight, and strengthening core muscles can also aid in prevention.

Alternative Therapies
- Options: Acupuncture, massage therapy, and yoga.
- Benefits: These therapies promote muscle relaxation, improve circulation, and help manage stress, all of which can contribute to pain relief.
When to See a Doctor
While many instances of sudden lower back pain improve with rest and home care, certain symptoms warrant medical attention:
- Pain Persists Beyond a Few Days: Chronic pain lasting more than a week may signal an underlying issue that requires medical evaluation.
- Radiating Pain or Numbness: If pain spreads down the leg or you experience numbness, tingling, or weakness, nerve involvement may be present.
- Loss of Bowel or Bladder Control: This rare symptom could indicate a serious condition known as cauda equina syndrome, requiring immediate medical attention.
Why Choose Alleviate Pain Clinic for Back Pain Relief?
At Alleviate Pain Clinic, we understand how disabling a shooting pain in the back when bending over can be. Our team specializes in evidence-based, non-surgical treatments designed to target the root cause of lumbar discomfort. From regenerative therapies such as prolotherapy and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) to guided physiotherapy and posture correction, every patient receives personalized care. If you have wondered, “How to relieve sharp lower back pain without long-term medication or invasive surgery?”, our integrative approach offers safe and lasting relief. Choosing our back pain treatment means gaining access to expert spine specialists, advanced diagnostics, and holistic recovery strategies.
FAQs About Sharp Lower Back Pain When Bending
Sudden pain may occur from muscle strain, ligament sprain, disc irritation, or joint misalignment. Bending stresses the lumbar spine, triggering sharp discomfort that needs careful evaluation.
No, shooting pain when bending indicates nerve involvement, often from a disc bulge, herniation, or irritation. While occasional strain resolves, persistent sharp pain requires medical assessment.
- Sharp lower back pain from strain usually improves within days to weeks with rest and care. Persistent or worsening pain beyond two weeks needs medical attention.
Causes include muscle strain, ligament injury, disc problems, or nerve compression. Sudden pain while bending forward signals stress on spinal structures and should not be ignored.
Relief may include rest, gentle stretches, posture correction, heat therapy, and strengthening exercises. If pain persists, consult a specialist for an accurate diagnosis and non-surgical treatment.





