Shoulder pain is a prevalent complaint that can have various causes, ranging from minor injuries to more serious underlying conditions. In this blog, we will explore 15 common causes of shoulder pain and highlight effective treatment options, with a focus on PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) and prolotherapy. At Alleviate Pain Clinic, we follow a multidisciplinary approach that incorporates image-guided stem cells, PRP, and prolotherapy, along with structured physical therapy regimes for managing these conditions. We will also address key questions regarding symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment.
What Is Shoulder Pain & Why It Happens?
The shoulder is an extremely mobile joint that permits movement of the arm in various directions, which is prone to wear and tear and damage. The causes of shoulder pain may be overuse of muscles, tendon rupture, joint inflammation, or degenerative processes. Timely assessment and treatment are essential to avoid the progression of the symptoms and chronic disability.
Overview of Shoulder Joint Anatomy
The shoulder joint is made up of three bones: the humerus (upper arm bone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the clavicle (collarbone). It is sustained by muscles, tendons, and ligaments, including the rotator cuff, which stabilises and moves the joint. With such a complex structure, the most insignificant injuries may cause front shoulder pain or radiating pain.
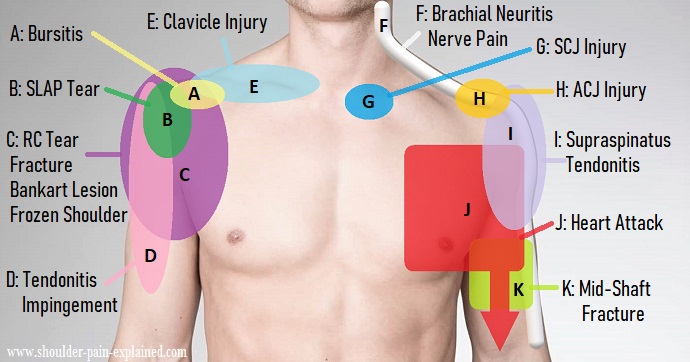
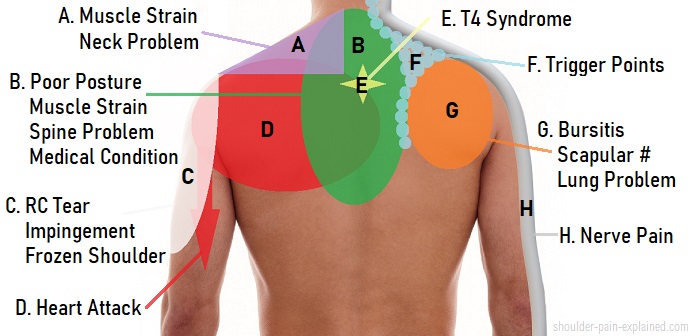
Top 15 Causes of Shoulder Pain
The most common causes of shoulder pain are due to injuries to the rotator cuff, bursitis, tendonitis, arthritis, and frozen shoulder. These problems commonly occur due to heavy lifting, overhead sports, or poor posture. Chronic strain can also cause stiffness and loss of range of motion, adding to both anterior and posterior shoulders as causes of pain in patients.
Common causes of shoulder pain
Impingement Syndrome
Impingement syndrome occurs when the rotator cuff tendons become irritated or pinched between the acromion and the humerus. Symptoms include pain, especially when lifting the arm. Treatment often includes rest, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications. In severe cases, PRP and prolotherapy can provide effective relief.
Rotator Cuff Tear
A rotator cuff tear is a tear in one or more of the tendons that make up the rotator cuff. Symptoms include persistent pain and weakness. Treatment may include physical therapy, PRP injections, or, in severe cases, surgery.
Rotator Cuff Tendonitis
Tendonitis is inflammation of the rotator cuff tendons. Symptoms include pain when lifting the arm and difficulty sleeping on the affected side. Treatment often involves rest, physical therapy, and PRP injections.
Frozen Shoulder/Adhesive Capsulitis
Frozen shoulder results in restricted movement and persistent pain. Treatment includes physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, hydodilatation and manipulation,and sometimes corticosteroid injections, hydodilatation and manipulation .PRP and prolotherapy can also be effective in relieving symptoms.
Acromioclavicular Joint Arthritis
Arthritis in the acromioclavicular joint can lead to shoulder pain. Treatment may include rest, anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, steroid injections, PRP injections.
Shoulder Arthritis
Shoulder arthritis causes pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion. Treatment options may include Stem cell, Viscosupplementation ,PRP injections and, in advanced cases, surgical interventions.
Labral Tear (SLAP Lesion)
A labral tear, especially a superior labral tear from anterior to posterior (SLAP lesion), can cause pain and instability. Treatment may involve PRP and prolotherapy injections and, in some cases, surgical repair.
Subacromial Bursitis
Subacromial bursitis is inflammation of the bursa in the subacromial space. Treatment includes rest, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and PRP injections for refractory cases.
Subdeltoid Bursitis
Inflammation of the subdeltoid bursa can result in pain and discomfort. Treatment may involve rest, anti-inflammatory medications, and PRP injections if conservative measures fail.
Bicipital Tendonitis
Tendonitis of the biceps tendon can cause anterior shoulder pain. Treatment options include rest, physical therapy, and PRP injections for pain relief and tendon healing.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic condition that can affect the shoulder joint. Treatment may involve medication, physical therapy, and PRP injections for symptom management.
Trauma
Shoulder injuries due to accidents or falls can cause pain and dislocations. Treatment depends on the type and severity of the injury and may include immobilization, physical therapy, and, in some cases, surgery.
Trigger Points
Muscle trigger points can refer pain to the shoulder. Treatment involves manual therapy, myofascial release, and PRP injections to alleviate pain and improve muscle function.
Instability
Shoulder instability can result from ligament or labral injuries. Treatment may include physical therapy and, in some cases, surgical stabilization. PRP and prolotherapy can aid in the healing process.
Calcific Supraspinatus Tendonitis
This condition involves calcium deposits in the supraspinatus tendon, leading to pain. Treatment options include rest, physical therapy, and PRP injections for reducing pain and promoting tissue healing.
How Is Shoulder Pain Diagnosed?
Diagnosis often involves a physical examination, imaging studies such as X-rays,Diagnostic Ultrasound or MRI, and, in some cases, diagnostic injections. MRI is often the gold standard Investigation of choice in diagnosing Rotator cuff pathology and Instability. A comprehensive evaluation by a medical professional is crucial for an accurate diagnosis.
Physical Examination & Medical History
An effective diagnosis starts with the investigation of a complete medical history and clinical examination. The doctor examines whether the pain starts or gets worse, and under which activities. The physical tests are useful in detecting range of motion restriction, muscular weakness, or joint instability, and this gives clues to diagnose the reasons for shoulder pains properly.
Imaging Tests (MRI, X-Ray, Ultrasound)
In case physical evaluation proves unclear, imaging is suggested. X-rays detect bone injuries, whereas ultrasounds detect tendon or soft tissue injuries. MRI can provide a detailed image of the cartilage, ligaments, and damage to the rotator cuff. Those tests prove the causes of shoulder pain and direct specific shoulder pain treatment regimes.
Non-Surgical Shoulder Pain Treatment
Shoulder pain treatment options depend on the specific condition but may include rest ,physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and in many cases, PRP and prolotherapy to promote healing and alleviate pain. Home remedies may include heat or cold therapy and gentle stretching exercises.
Home Remedies for Shoulder Pain Relief
To relieve mild to moderate pain, just making a few lifestyle changes may be enough. Rest, ice, and over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications all help to decrease pain and swelling. Light stretching, posture correction, and avoiding repetitive overhead activities also help in the recovery process. These have the ability to be used alongside medical care in providing front shoulder pain.
Conclusion
Shoulder pain can result from a variety of causes, and effective treatment options are available. At Alleviate Pain Clinic, a multidisciplinary approach, including PRP, prolotherapy, and physical therapy, is employed to provide relief for various shoulder conditions. Early diagnosis and proper treatment can help individuals regain their shoulder function and quality of life.
References
- Maund, Joseph R., et al. Ultrasound-guided subacromial corticosteroid injections are more effective than landmark-guided injections: a randomised double-blind study. British Journal of Sports Medicine 48.16 (2014): 1202-1207.
- Porat, Susan, and James May. Ultrasound-guided injection of the subacromial bursa with a local anesthetic and corticosteroid in patients with possible rotator cuff impingement: does it work?. Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery 24.6 (2015): e131-e132.
- Ludvig, Ina Lian, and Jan E. Hoff. Shoulder injuries from shot firing: a new risk group. BMJ case reports 2012 (2012): bcr2012006742.
- Baddeley, Rachel, and Philip Davidson. Ultrasound-guided subacromial bursa injections are effective for persistent rotator cuff disease Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 8.1 (2013): 18.
- Gilmore, Brice, et al. Ultrasound-guided injections of the acromioclavicular joint: a posterior approach. Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine 33.12 (2014): 2127-2130.
- Malavolta, Eduardo Angeli, et al. Platelet-rich plasma in rotator cuff repair: a prospective randomized study. The American Journal of Sports Medicine 44.9 (2016): 2259-2266.
- Rees, Jonathan D., Roger Maffulli,
Frequently Asked Questions
The most common shoulder pain includes rotator cuff injuries, tendonitis, bursitis, frozen shoulder, arthritis, and impingement syndrome. Repetitive movements, poor posture, and trauma also contribute. In some cases, posterior shoulder pain causes like labral tears or instability are involved. Early diagnosis helps prevent worsening. Consulting a doctor ensures proper shoulder pain treatment and prevents long-term complications affecting mobility and quality of life.
Yes, PRP therapy is an advanced regenerative option for chronic shoulder pain treatment. It uses concentrated platelets from the patient’s blood, injected into the affected joint or tendon, to stimulate natural healing. PRP can reduce inflammation, repair microtears, and improve function in conditions like rotator cuff injuries or tendonitis. Patients with long-standing pain who don’t respond to medications or physiotherapy may benefit significantly from PRP as a minimally invasive treatment.
Recovery from shoulder tendonitis depends on severity and treatment. Mild cases may improve in 2–4 weeks with rest, ice, and activity modification. Moderate to severe tendonitis can take 6–12 weeks with physiotherapy and strengthening. If advanced therapies like PRP or prolotherapy are used, healing may accelerate. Persistent or untreated tendonitis can progress to chronic shoulder pain, requiring longer rehabilitation. Consistent treatment and avoiding aggravating movements help ensure faster recovery.
Bursitis involves inflammation of the bursa, a fluid-filled sac cushioning the joint, often triggered by repetitive friction. Tendonitis is inflammation of the shoulder tendons, typically caused by overuse or strain. While both conditions cause shoulder pain, bursitis often leads to swelling and tenderness, whereas tendonitis results in movement-induced pain. Differentiating these conditions through clinical examination and imaging is essential, as management varies, ranging from physiotherapy to injections for effective shoulder pain treatment.
You should consult a doctor if shoulder pain persists beyond two weeks, worsens at night, or restricts arm movement. Sudden front shoulder pain after injury, weakness, or visible deformity requires immediate medical attention. Symptoms like swelling, joint instability, or persistent stiffness may indicate underlying shoulder pain causes such as rotator cuff tears, arthritis, or bursitis. Early diagnosis and shoulder pain treatment help prevent long-term damage and restore normal mobility effectively.






