Introduction
Inner knee pain, also known as medial knee pain, can significantly disrupt daily activities and limit mobility. It affects people of all ages and can result from various causes, ranging from injuries to chronic conditions. Understanding the underlying reason for inner knee pain is essential for effective treatment. This blog explores the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, including regenerative medicine and surgery, and highlights the multidisciplinary approach followed at Alleviate Pain Clinic, Bengaluru, to provide holistic care.
Causes of Pain on the Inner Side of the Knee and Their Associated Symptoms
To better understand inner knee pain, it is important to correlate the causes with the specific symptoms. This helps patients identify what might be causing their discomfort and allows clinicians to focus on targeted treatment. Below is a detailed correlation between common causes and their associated symptoms.
Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Injury
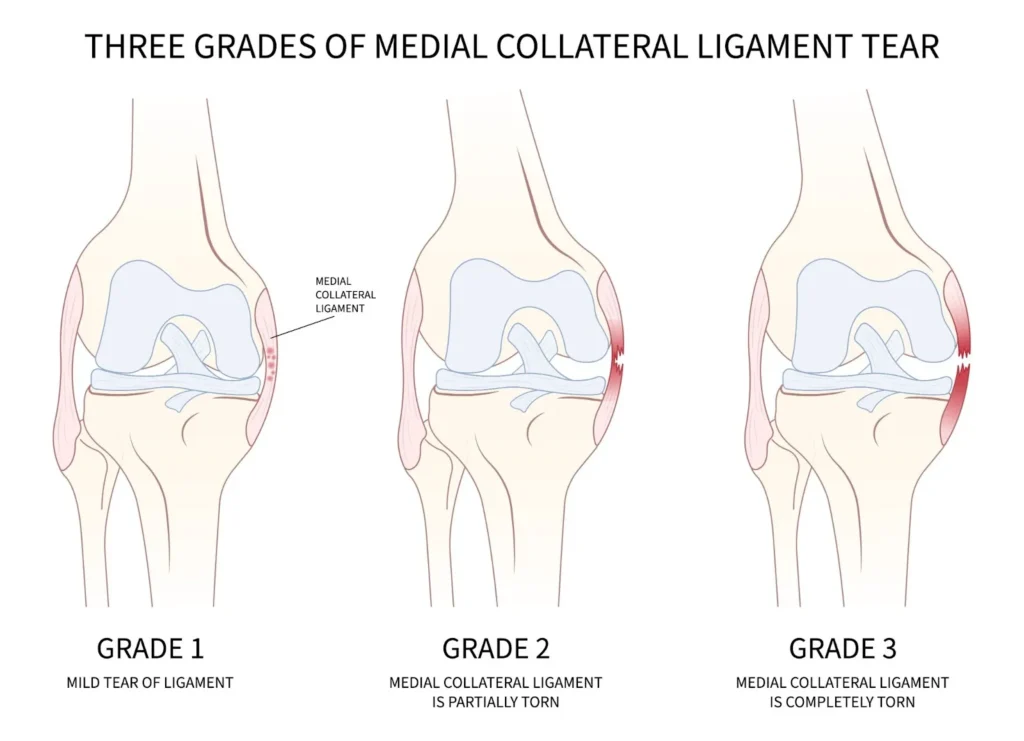
Cause
Sprain or tear of the MCL due to trauma, sudden twisting, or a blow to the outside of the knee (common in sports).
Symptoms
- Sharp pain along the inner side of the knee.
- Swelling shortly after injury.
- Instability or a sensation that the knee might give way.
- Tenderness when pressing along the inner knee.
- Limited range of motion due to pain and stiffness.
Meniscus Tear (Medial Meniscus)
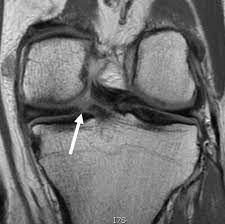
Cause
Twisting or rotating the knee forcefully, such as during sports activities or heavy lifting. Degenerative tears can occur with age-related wear.
Symptoms
- Pain during movement or weight-bearing, especially when twisting the knee.
- Swelling that develops over several hours or the next day.
- Clicking, locking, or catching sensation in the knee.
- Stiffness or inability to fully straighten the knee.
- Pain may increase with stairs, squats, or deep bending.
Osteoarthritis of the Knee
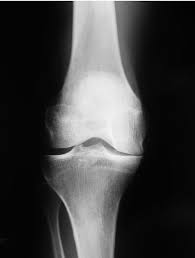
Cause
Gradual wear and tear of the cartilage, leading to bone-on-bone friction, common in older adults or individuals with excess weight.
Symptoms
- Dull, aching pain on the inner side of the knee.
- Morning stiffness or stiffness after prolonged inactivity.
- Cracking or grinding sounds (crepitus) during knee movement.
- Pain that worsens with activity and improves with rest.
- Swelling and tenderness around the joint, especially after long walks.
Pes Anserine Bursitis
Cause
Inflammation of the bursa located near the inner knee, often caused by overuse, improper footwear, running, or sudden increases in physical activity.
Symptoms
- Localized pain and tenderness about 2-3 inches below the knee joint.
- Pain worsens with climbing stairs, kneeling, or sitting cross-legged.
- Swelling around the inner knee.
- Pain may worsen at night or after physical exertion.
Medial Plica Syndrome
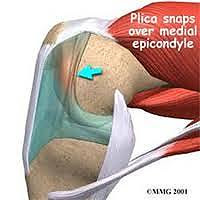
Cause
Inflammation or irritation of the plica, a fold of synovial tissue, due to repetitive knee movements or overuse.
Symptoms
- Sharp or dull pain along the inner knee, typically during activity.
- Clicking or snapping sensation when bending or straightening the knee.
- Pain aggravated by prolonged sitting or climbing stairs.
- Swelling or warmth around the knee joint.
Traumatic Knee Injury (Fractures or Contusions)
Cause
Direct trauma to the knee from falls, accidents, or collisions, causing fractures or soft tissue damage.
Symptoms
- Severe pain immediately after the injury.
- Swelling and bruising around the knee.
- Inability to bear weight on the affected leg.
- Visible deformity or abnormal movement in severe fractures.
Patellar Subluxation or Maltracking
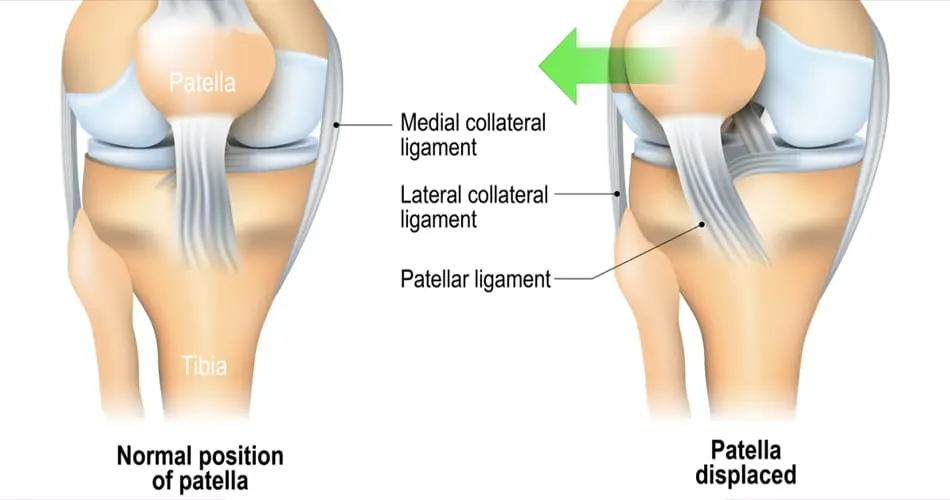
Cause
The kneecap (patella) shifts out of its normal alignment, causing friction with the underlying bone and tissues. It can result from muscle imbalance, trauma, or congenital factors.
Symptoms
- Pain on the inner side of the knee due to irritation from the displaced patella.
- Feeling of instability, with the knee giving way.
- Popping or clicking sensation during movement.
- Pain worsens with stairs, running, or squatting.
Correlation Table: Causes vs. Symptoms
| Cause | Primary Symptoms | Additional Features |
| MCL Injury | Sharp inner knee pain, swelling, instability, tenderness | Occurs after trauma or twisting; worse with side-to-side movements |
| Meniscus Tear | Pain during twisting or weight-bearing, swelling, clicking/locking sensation | Pain increases with squats, stairs; stiffness after rest |
| Osteoarthritis | Dull pain, morning stiffness, crepitus, swelling | Pain improves with rest; worse with activity and prolonged sitting |
| Pes Anserine Bursitis | Localized pain 2-3 inches below knee, swelling, pain with stairs or kneeling | Pain worsens at night or after exercise |
| Medial Plica Syndrome | Sharp/dull pain, snapping sensation, aggravated by prolonged sitting | Pain increases with stair climbing and repetitive bending |
| Fracture or Trauma | Severe pain, swelling, bruising, deformity | Inability to bear weight; immediate onset after injury |
| Patellar Subluxation/Maltracking | Inner knee pain, popping sensation, instability | Pain worsens with stairs, running, or squatting |
Diagnosis of Medial Knee Pain
Physical tests such as the valgus stress test or McMurray’s test help identify ligament or meniscal injuries.
Imaging Techniques
- X-rays are useful to detect fractures or arthritis.
- MRI scans provide detailed images of soft tissues like the meniscus, ligaments, or cartilage.
- Ultrasound may be used to assess bursitis or plica syndrome.
Blood Tests
In cases where infections or inflammatory conditions like gout are suspected, blood tests may be required.
Treatment Options for Inner Knee Pain
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is often the first line of treatment for non-traumatic inner knee pain. It focuses on improving strength, flexibility, and stability.
- Strengthening exercises: Target quadriceps, hamstrings, and hip muscles to support the knee joint.
- Stretching routines: Focus on the IT band, hamstrings, and calves.
- Taping or bracing: Helps improve knee alignment and reduce strain.
- Electrotherapy: Modalities like ultrasound or TENS reduce pain and inflammation.
Medications
Medications help relieve pain and inflammation to allow better participation in therapy.
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Ibuprofen or naproxen for pain relief.
- Corticosteroid injections: For temporary relief from inflammation and swelling.
- Analgesics: Painkillers for acute or chronic pain.
Regenerative Medicine for Knee Pain
Regenerative medicine is an advanced treatment option that promotes healing by using the body’s natural healing mechanisms. It is highly effective for degenerative conditions like osteoarthritis and tendon injuries.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: Involves injecting concentrated platelets to promote tissue repair and reduce inflammation.
- Prolotherapy: A regenerative injection therapy that stimulates the body’s healing response, helping to repair damaged ligaments and tissues.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Uses mesenchymal stem cells to regenerate cartilage, reduce inflammation, and restore knee function.
These treatments are minimally invasive and promote long-term healing, making them ideal for patients seeking alternatives to surgery.
Surgical Options
In cases where conservative treatments fail, surgery may be necessary.
- Arthroscopic Surgery: Minimally invasive surgery to remove damaged cartilage, repair meniscal tears, or realign the patella.
- Knee Replacement Surgery: In advanced osteoarthritis cases, a partial or total knee replacement may be required to restore function.
- MCL Repair or Reconstruction: For severe ligament injuries, surgery may involve repairing or reconstructing the MCL.
The Multidisciplinary Approach at Alleviate Pain Clinic, Bengaluru
At Alleviate Pain Clinic, we believe that treating inner knee pain requires more than just addressing symptoms. Our multidisciplinary approach ensures that patients receive comprehensive care through a blend of:
- Interventional Pain Management: Procedures like PRP injections or nerve blocks to manage pain and promote healing.
- Physiotherapy: Individualized exercise programs tailored to each patient’s needs.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Guidance on weight management, proper footwear, and activity modifications.
- Psychological Support: Chronic knee pain can affect mental well-being, and our team offers counseling or mindfulness techniques to improve emotional health.
- Post-Treatment Rehabilitation: Ongoing monitoring and follow-ups to ensure long-term recovery and prevent recurrence.





