
Experiencing left-sided neck pain can disrupt daily activities and make even simple movements uncomfortable. Left-sided neck pain is a common complaint with various potential causes, ranging from poor posture to more serious underlying conditions. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the causes of left-sided neck pain, symptoms to watch for, and treatment options to help alleviate discomfort.
What Causes Neck Pain on the Left Side?
Poor Posture and Muscle Strain
Poor posture, especially while sitting at a desk or using mobile devices, can strain the muscles on the left side of the neck.
- How It Happens: When the head is constantly tilted forward or to one side, the muscles in the neck have to work harder to support the head. Over time, this can lead to tension and muscle strain.
- Symptoms: Dull, aching pain on the left side of the neck that worsens after long periods of poor posture, stiffness, and muscle tightness.
- Risk Factors: Long hours sitting at a computer, looking down at a phone, or reading in bed without neck support.

Cervical Muscle Strain or Sprain
Overstretching or tearing of the muscles or ligaments on the left side of the neck can lead to a strain or sprain.
- How It Happens: Sudden movements, lifting heavy objects, or sleeping in an awkward position can overstretch or tear neck muscles.
- Symptoms: Sharp pain, tenderness, and limited range of motion on the left side of the neck.
- Risk Factors: Sudden jerking motions, lifting with poor posture, or physical activities that overstrain the neck muscles.

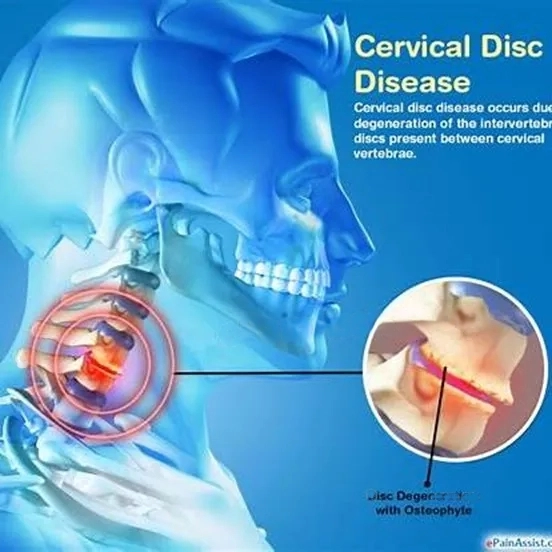
Cervical Disc Degeneration
The cervical spine, or neck area of the spine, contains discs that act as cushions between the vertebrae. Degeneration of these discs can cause left-sided neck pain.
- How It Happens: Age-related wear and tear can cause the discs in the cervical spine to lose their flexibility, resulting in pain and stiffness.
- Symptoms: Chronic, aching pain on one side of the neck, which may worsen with activity. In some cases, pain may radiate into the shoulder or arm.
- Risk Factors: Aging, repetitive movements, and heavy lifting can accelerate cervical disc degeneration.
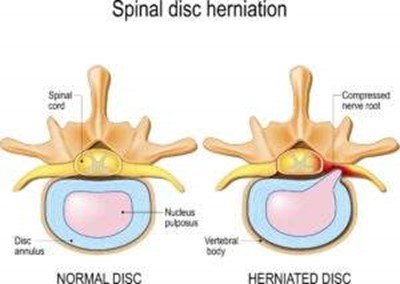
Cervical Disc Bulge/ Herniation
A herniated disc occurs when the inner gel of the disc pushes out through a tear in the outer layer, potentially pressing on nearby nerves. Pain maybe discogenic or radicular
- How It Happens: A herniated disc can result from a sudden injury or from gradual wear and tear. If the herniation is on the left side, it may cause pain specifically on that side.
- Symptoms: Sharp, radiating pain on the left side of the neck, potentially radiating down the left arm. Numbness or tingling in the shoulder or fingers may also be present.
Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve)
Cervical radiculopathy occurs when a nerve in the neck becomes compressed or irritated, causing pain to radiate from the neck to other areas.
- How It Happens: A pinched nerve from a herniated disc, bone spur, or spinal stenosis can cause left-sided neck pain.
- Symptoms: Sharp, burning pain on the left side of the neck, often extending to the shoulder, arm, or hand. May also cause tingling, numbness, or weakness.
- Risk Factors: Arthritis, repetitive neck movements, heavy lifting, or spinal conditions that narrow the spaces where nerves pass.
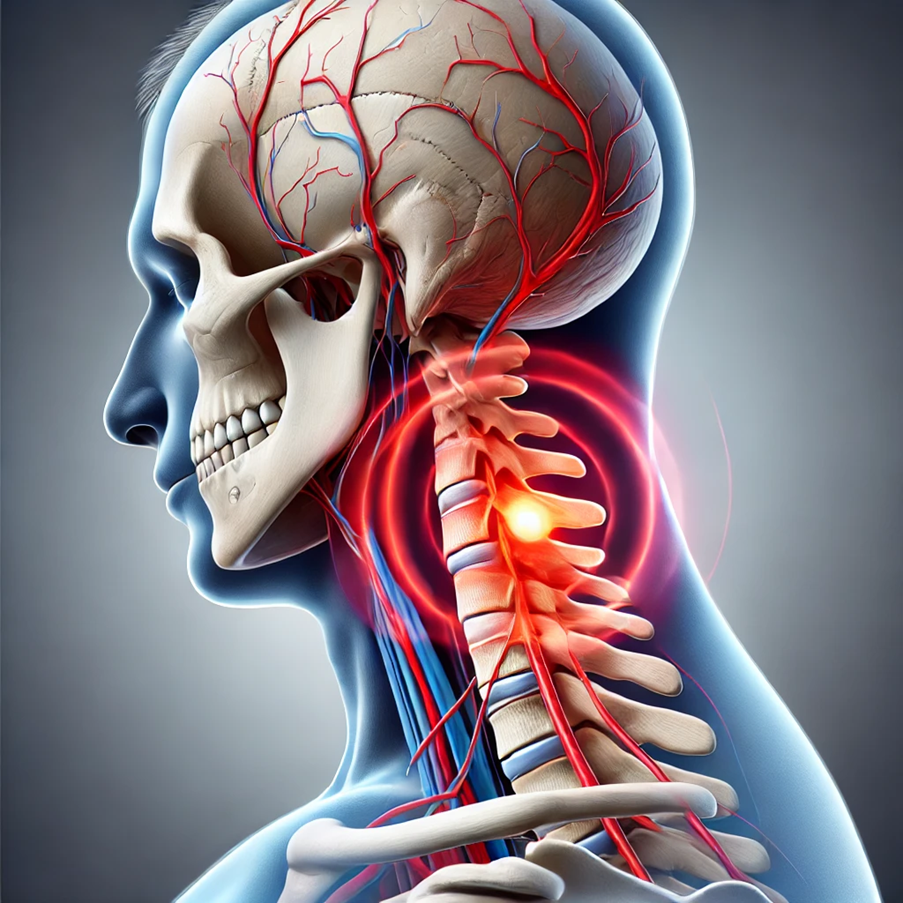
Pinched nerve due to a cervical disc herniation causing radiculopathy
Whiplash
Whiplash is a neck injury that occurs from a sudden, forceful back-and-forth movement of the neck, commonly seen in car accidents.
- How It Happens: The sudden jerking motion can strain muscles and ligaments on the left side of the neck, leading to pain and stiffness.
- Symptoms: Sharp pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility on the left side. Headaches, dizziness, or tingling in the arms may also occur.
- Risk Factors: Car accidents, high-impact sports, or any sudden impact to the neck.
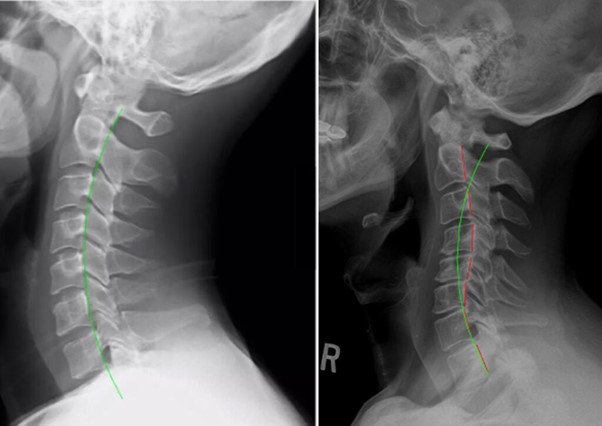
Cervical spine malalignment and loss of normal curvature as seen on the x-ray of a post whiplash injury patient
Arthritis in the Cervical Spine
Osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis can affect the facet joints of the cervical spine causing inflammation and pain.
- How It Happens: Arthritis leads to the breakdown of cartilage between the joints in the neck, causing pain and stiffness on the left side if the joints there are affected.
- Symptoms: Chronic, dull pain on the left side of the neck when the facet articulation on the left side is more affected, stiffness, and limited range of motion. In severe cases, nerve compression may cause tingling or numbness.
- Risk Factors: Aging, family history of arthritis, obesity, or previous neck injuries.
Text Neck Syndrome
- How It Happens: Constantly looking down at screens puts strain on the cervical spine, causing pain, often on one side.
- Symptoms: Dull, aching pain on the left side of the neck, shoulder pain, and headaches.
- Risk Factors: Excessive smartphone use, lack of posture awareness, and long hours on digital devices.

Infections and Inflammatory Conditions
Infections such as meningitis or inflammatory conditions like ankylosing spondylitis can cause left-sided neck pain.
- How It Happens: Infection or inflammation of neck tissues can result in localized pain.
- Symptoms: Stiff neck, fever (in infections), fatigue, and widespread pain (in inflammatory conditions).
- Risk Factors: Exposure to infections, autoimmune conditions, and chronic inflammatory conditions.
Trigger Points and Myofascial Pain
Syndrome Myofascial pain syndrome is a chronic pain condition that involves sensitive areas in the muscles, known as trigger points. When these trigger points are pressed, they cause localized pain and sometimes radiate discomfort to other areas, including the neck.
- How It Happens: Trigger points can form due to repetitive strain, stress, or muscle injuries, resulting in tight muscle knots that lead to pain. If located on the left side of the neck, they can cause persistent pain that may feel like a dull ache or sharp discomfort.
- Symptoms: Localized pain in the neck, muscle stiffness, and referred pain to nearby areas, which can limit mobility.
- Risk Factors: Physical or emotional stress, repetitive neck strain, poor posture, and prior muscle injuries.
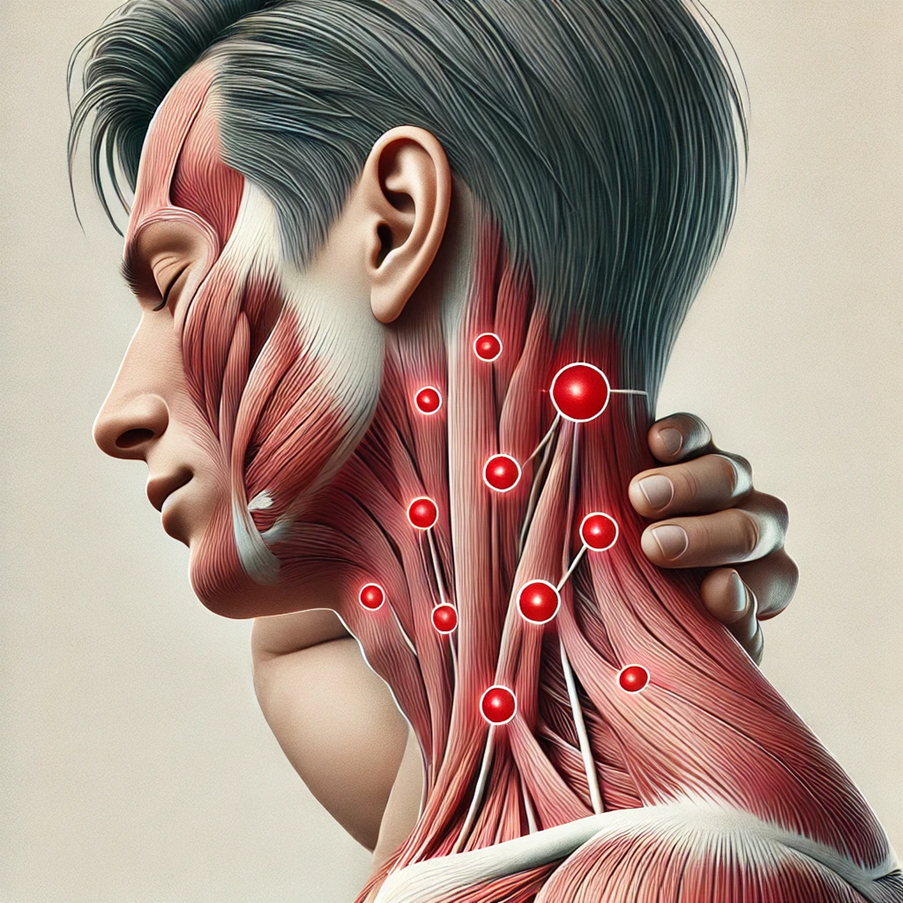
Typical trigger points causing left sided neck pain depicted in the figure.
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, which can often manifest as pain in the neck and shoulders.
- How It Happens: The exact cause of fibromyalgia is unknown, but it’s believed to involve abnormal pain processing in the brain and may be triggered by physical or emotional trauma.
- Symptoms: Diffuse pain in the neck and other body parts, fatigue, stiffness, and tenderness. Neck pain may appear on one side or both, often worse with physical activity or stress.
- Risk Factors: Family history of fibromyalgia, history of arthritis or other pain conditions, physical or emotional stress, and sleep disturbances.
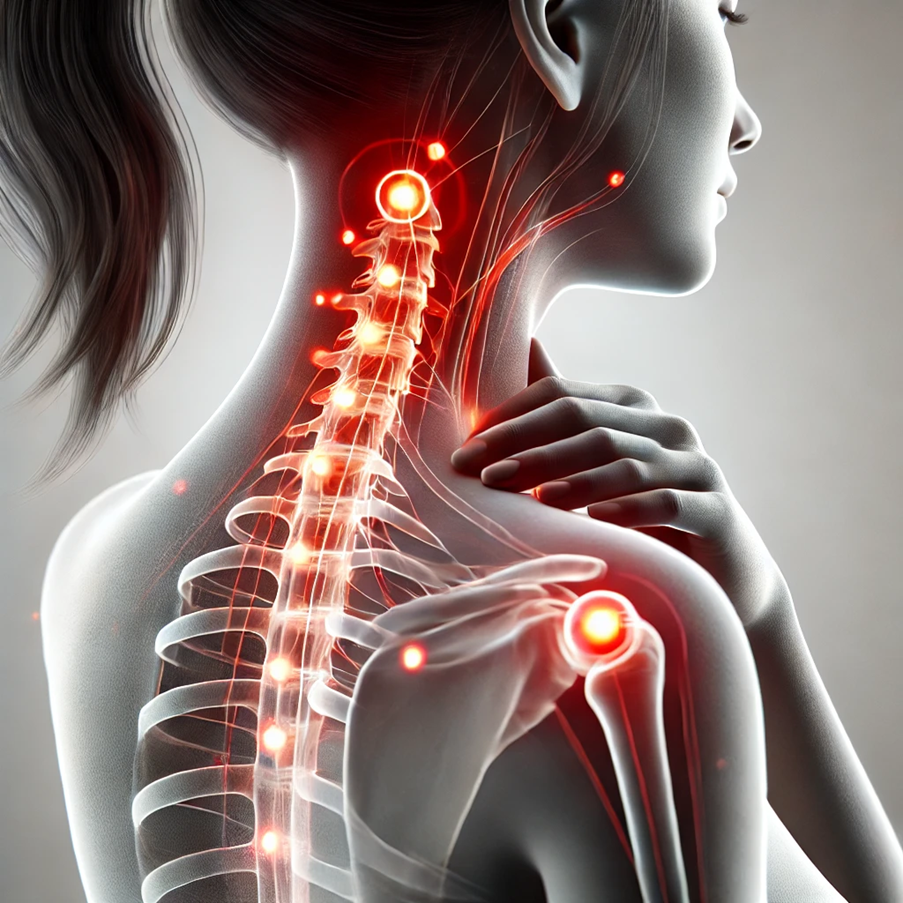
Neck pain along with widespread tender points can be an ususal presentation in Fibromyalgia
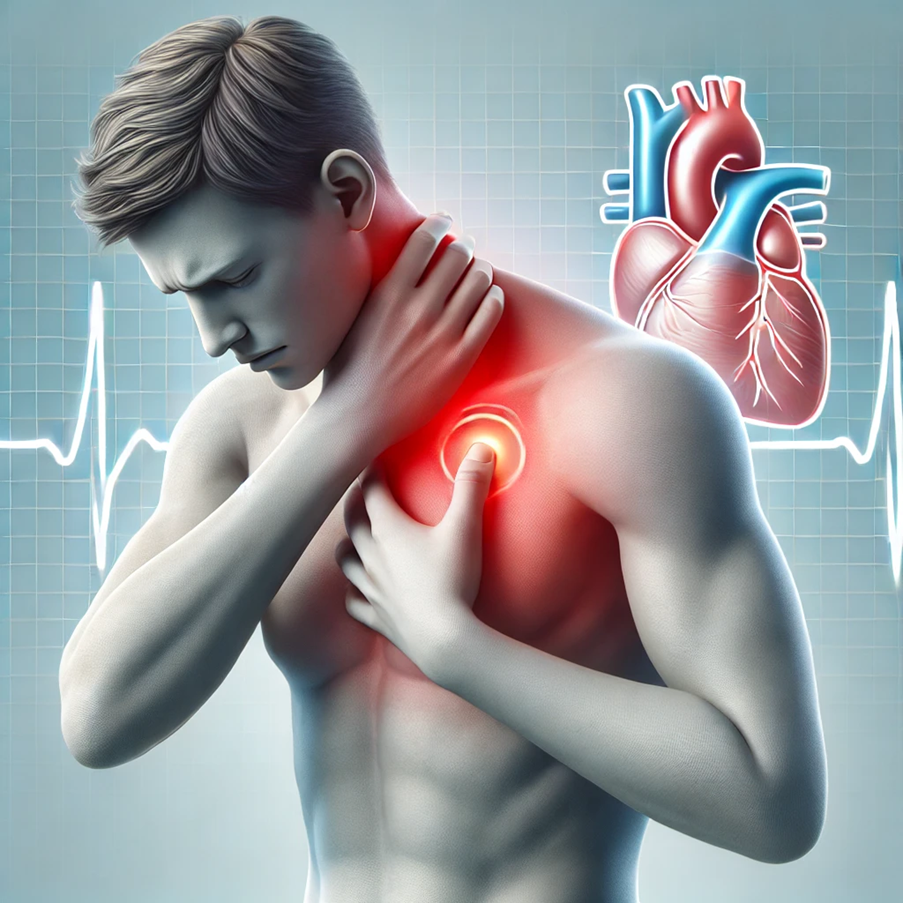
Heart-Related Issues
- Although rare, left-sided neck pain can be a symptom of heart-related issues, particularly in cases of angina or heart attack.
- How It Happens: Heart-related pain can radiate to different areas, including the neck and left arm.
- Symptoms: Sudden, intense pain on the left side of the neck, accompanied by chest pain, shortness of breath, and sweating.
- Risk Factors: Family history of heart disease, smoking, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Left-Sided Neck Pain
While left-sided neck pain is often due to muscle strain or posture issues, certain symptoms may indicate a more serious condition. Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Severe, sudden pain that does not improve with rest
- Pain that radiates down the arm or causes numbness or weakness
- Persistent pain that lasts for more than a week
- Accompanying symptoms like fever, headache, or dizziness
- Chest pain, shortness of breath, or sweating (could indicate heart-related issues)
Neck Pain Left Side Treatment Options
Rest and Lifestyle Modifications
- Avoid activities that aggravate the pain and incorporate regular breaks to reduce neck strain.
- Maintain good posture and use ergonomic equipment if working long hours on a computer.
Physical Therapy
- A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise plan to strengthen neck and shoulder muscles.
- Manual therapy and gentle stretching help relieve muscle tension and improve flexibility.
Pain Relief Medication
- Over-the-counter pain relievers, like ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can reduce pain and inflammation.
- In cases of severe pain, a doctor may prescribe stronger medication or muscle relaxants.
Heat and Cold Therapy
- Ice packs reduce inflammation and numb acute pain; heat packs relax muscles and improve blood flow.
- Alternate between heat and cold therapy, applying for 15-20 minutes as needed.
Chiropractic Adjustments
- Chiropractors can perform spinal adjustments to relieve pressure on the neck and restore alignment.
- Chiropractic care may help reduce pain caused by poor posture, muscle strain, or spinal misalignment.
Interventional Pain Management
- Trigger Point Injections: For muscle-related pain, injections can provide targeted relief.
- Epidural Steroid Injections: For pain caused by herniated discs or nerve compression, steroids reduce inflammation and pain.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): PRP injections use growth factors from the patient’s own blood to promote tissue repair and relieve chronic neck pain.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Stem cells may support cartilage regeneration in degenerative conditions affecting the cervical spine.
Mindfulness and Stress Management
Stress and anxiety can increase muscle tension in the neck. Practices like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help manage stress and reduce tension.
How to Relieve Severe Neck Pain on the Left Side?
- Posture Awareness: Maintain a neutral spine while working, driving, or using mobile devices.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Use a chair with lumbar support, adjust your monitor to eye level, and keep your feet flat on the floor.
- Frequent Breaks: Take breaks every 30 minutes when working on a computer or using mobile devices to reduce strain on the neck.
- Proper Sleep Position: Use a supportive pillow that keeps your neck in a neutral position, and avoid sleeping on your stomach, which can strain the neck.
- Strengthening Exercises: Regularly perform neck and shoulder strengthening exercises to improve posture and reduce muscle imbalances.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration supports spinal disc health, reducing the risk of degenerative disc issues.
- Limit Heavy Lifting: Avoid lifting heavy objects in a way that strains the neck, and practice proper lifting techniques by using your legs rather than your back or neck.
Best Exercises for Left-Sided Neck Pain Relief
Physical activity is crucial in neck pain recovery. In the hands of an expert, you will be able to enjoy:
- Chin Tucks: Helps to build the deep neck muscles and correct posture
- Neck Side Bends: Stretches lateral neck muscles loosely
- Shoulder Blade Squeezes: Releases upper back and neck tension
- Neck Rotation: Increases range of motion and improves stiffness
These exercises should be performed slowly, and sudden movements must be avoided; otherwise, they should be stopped. At Alleviate Pain Clinic, physiotherapists provide tailored exercise programs to patients to keep them safe and effective.
Prevention Strategies for Left-Sided Neck Pain
- Keeping screens at eye level to avoid bending the neck forward
- Taking breaks from prolonged sitting or computer use
- Using supportive pillows that align the head and spine
- Staying active to maintain flexibility and muscle strength
- Managing stress to prevent tension-related neck stiffness
Consistent preventive measures reduce the risk of recurrence and support spinal health over time.
Expert Tips for Managing Chronic Left-Sided Neck Pain
Chronic neck pain needs to be treated using lifestyle and medical interventions. Improvement in posture is achieved by strengthening of supporting muscles through routinely conducted physiotherapy sessions. Designs of workspaces reduce stress induced during the day-to-day events. Stress Management techniques like yoga or meditation can alleviate the pain due to tension since it is a tension reduction technique. Recovery of muscles will take place with the help of sleep and sufficient fluid consumption. In cases of chronic pain or pain intensification, consulting with a pain specialist at Alleviate Pain Clinic helps to ensure a correct diagnosis so that the patient can receive the appropriate, non-surgical method of relieving pain once and forever.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What causes sudden, severe neck pain on the left side?
Sudden severe neck pain on the left side can result from muscle strain, nerve compression, cervical disc problems, or injury. Rarely, it may indicate heart-related issues or infections. Identifying the underlying cause through proper medical evaluation is essential to determine the correct treatment and prevent worsening of symptoms.
How long does left-sided neck pain usually last?
The duration depends on the cause. Minor muscle strain may improve within a few days with rest and gentle care, while conditions like herniated discs or arthritis may persist for weeks. Chronic cases require targeted treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and medical follow-up for long-term relief and to prevent recurrence.
Can sleeping position cause neck pain on the left side?
Yes. Sleeping with the neck twisted or on an unsupportive pillow can strain muscles and ligaments, leading to left-sided neck pain. Maintaining spinal alignment, using an ergonomic pillow, and avoiding stomach sleeping can help prevent discomfort and stiffness caused by poor sleeping posture over time.
Is left-sided neck pain a sign of heart problems?
Although uncommon, left-sided neck pain can be a warning sign of heart issues, particularly if accompanied by chest pain, shortness of breath, sweating, or nausea. Immediate medical attention is crucial in such cases to rule out cardiac emergencies and ensure timely diagnosis and treatment.
What are the best home remedies for severe left-sided neck pain?
Effective home remedies include applying warm or cold compresses, gentle stretching, over-the-counter pain relievers, and maintaining good posture. Short rest periods help, but prolonged inactivity should be avoided. If pain persists beyond a week or worsens, professional medical evaluation is recommended for safe and effective management.





